Which Device Is Used To Create A Physical Star Topology

1 of the first decisions you confront when setting up a network is what kind of 'topology' to use. The network topology dictates how different sender and receiver nodes communicate with each other. Each type of topology has its advantages and drawbacks, making information technology important to pick the setup that provides the all-time performance and stability for your network. Today, we volition focus on the most popular one: star topology.
What is network topology?
Much of the industrialized world runs on computers. Equally a upshot, we need a skilful deal of physical space to manage so many devices. Picture show computer labs, hospitals, offices, banks, schools, and airports. Not only do they take a lot of computing stations, but they have to accommodate vast networks that are extensive, safe, and powerful enough to back up a multitude of users at once.
Network topology is the physical and logical layout of the devices and connections that form your network. There are many unlike types of network topologies, and the right i to choose depends on your networking, space, and security needs.
Why is network topology important?
The bigger the network y'all're managing, the more physical space you lot demand for storing devices, such every bit commercial servers and routers. And each of these devices has multiple cable connections that must exist routed in a safe, orderly style, particularly in areas with foot traffic. Carefully planning out the physical placement of network components is crucial for many reasons:
- An optimized layout allows more infinite for devices and movement within the room.
- IT technicians need an easy way to observe connections and points of failure to service them.
- A poorly routed network is more prone to hazards and equipment failure.
The logical design of a network refers to how data flows through the network to back up your connectivity needs overall. Logical topology mapping helps to:
- Anticipate and combat potential connectivity issues
- Reduce operational costs by allocating network resources efficiently
- Amend network functioning and speed up information transfer rates
What is star network topology?
With a star topology setup, each node (such as a computer) within your visitor or squad connects to ane central network device (which could be a hub, a switch, or a figurer) via a cablevision. The cardinal network is the server, and the other devices are clients.
Star topology (or 'star network') is the almost widely used network for LANs. It was offset popularized by ARCnet, before being adopted by Ethernet.
If the nodes (or computers) want to communicate with each other, they pass the message on to the central server hub, which and then forwards that message dorsum on to the different nodes (computers). If you moving-picture show this flow of information, it looks similar a star — which is how this network got its proper name! When setting up a wide area network (WAN), we refer to this aforementioned star formation equally hub-and-spoke topology.
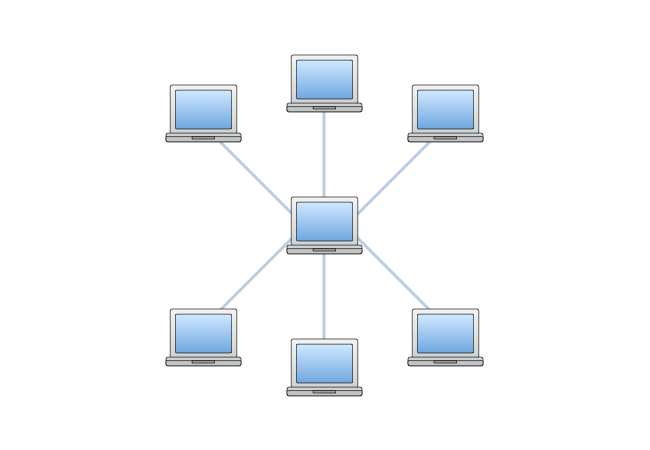
In some circles, this central node/hub is likewise called a 'root,' and the peripheral hosts are called 'leaves.'
How a star topology works
Let's say one computer wants to ship data to another computer. The first computer will forward the information to the hub. The hub will and then check the address of the recipient computer and frontwards the message on.
But the hub has no retentiveness of its ain, and so when the first computer sends over the information, the hub needs to ask all the other computers and ports which of them owns that address.
This procedure is Address Resolution Protocol (or ARP for brusque). Essentially, it means that the hub can find the right address of the recipient estimator and transfer the data to the right place.
In terms of cables, star topologies are sometimes implemented with Ethernet/cabled structures, wireless routers, and other components. These boosted nodes are clients and all link dorsum to the key hub.
Pros and cons of a star topology
No topology is perfect, and the star version has its off-white share of good and bad points.
Pros:
- If one node or connection breaks, the rest of the network remains unaffected. Other computers and their connections can continue working with zero downtime.
- Information technology's highly scalable. Y'all can add or remove new computers/devices without agonizing the whole network.
- Heavy loading = no sweat. Star networks can accommodate many different machines, which means it's possible to create an extensive network.
- Star networks are safer in the outcome of a cyber attack. Let's say you run a bank with several branches. If one branch or function comes under attack, the server will be notified and forbid a 2d. One branch goes downwardly, but the others keep running in complete safe. Phew!
Cons:
- Each cablevision individually connects to the cardinal server, which means you lot're going to need A LOT of cables. And that doesn't come cheap. Although, it's worth noting that the upfront cost of cables is a fraction of the cost of reanimation from a full system failure. Most network designers call up this do good far outweighs the cablevision price.
- The hub is a single signal of failure, which means it brings the whole network down if information technology stops.
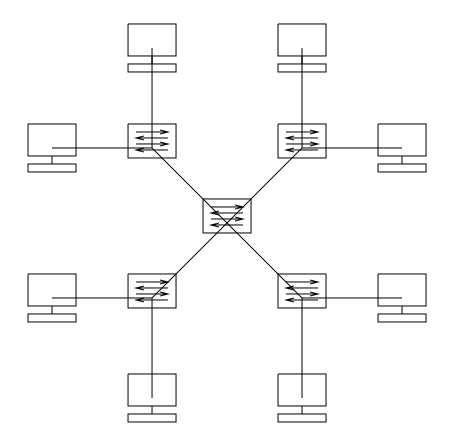
- In reality, there are only so many machines you lot can connect to a central server before you start running out of cable length and ports. I way effectually this is to blueprint an extended star topology by connecting multiple stars with a new key server in the eye. In this situation, messages from each system are transferred to its star, which transmits it to the cadre server, so back out to the star and the destination arrangement.
How to use a star topology diagram
Systems administrators and network designers accept lots to consider when planning and implementing a topology. I way to make this job a piddling easier is to create a network diagram to help you communicate your design, deployment, and topology plans across the team.
Presenting your star topology as a visual helps y'all plan, besides as identify any mismatched connections or weak points. Information technology also eliminates misunderstandings and mistakes inside your squad. Call back of it as a blueprint or map to your network layout.
Final thoughts
Using defended diagramming software can really take the stress out of designing your network. Rather than wrestling with clipart boxes and arrows, you can grab a template from a pre-made list and edit it with custom icons (including Amazon Web Services (AWS) icons and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) icons), arrows, boxes, and colors.
Plus, if yous're using Cacoo — our own diagramming tool — yous can store your diagrams in the cloud, share and consign everything in real-time, and permit simultaneous, tracked editing as you go. All of this means you tin can get your architecture setup just right the first time.
This post was originally published on April 12, 2019, and updated well-nigh recently on December 31, 2021.
Collaborate on ideas to align your team'southward vision in Cacoo
Which Device Is Used To Create A Physical Star Topology,
Source: https://cacoo.com/blog/get-server-setup-spot-on-star-topology/
Posted by: ratliffpeammeak.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Which Device Is Used To Create A Physical Star Topology"
Post a Comment